| Date | Class meetings notes and materials | HW assignments | |
| 05/23 | Final Exam, 2 pm - 3:50 pm, at CP 320 You can see your grades in Google Spreadsheet. The exam is closed book and closed notes, but you can use 3 cheat sheets (both sides used) Some interesting reads for the summer: 1) Finish Chapter 14 and do Chapter 15 from our textbook 2) Pointers vs References: http://www.cplusplus.com/articles/ENywvCM9/, https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/pointers-vs-references-cpp/ https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/passing-by-pointer-vs-passing-by-reference-in-c/ 3) Unique pointers (std::unique_ptr): https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/memory/unique_ptr http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/memory/unique_ptr/ |
||
| 05/16 | Final Exam preparation Final exam preparation slides (they don't have all the problems from Part 3). See the remaining problems in this file: finalExam_CSI33sample.pdf Solutions: FinalExam_CSI33sampleSols.pdf, BFSproblem.pdf, product.cpp. |
||
| 05/11 | Sections 14.3 - 14.4 Lecture slides: CSI33-lecture25.pdf Program: DisjointSet.py A short (~2mins) but very nice video of depth first search algorithm application: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mE_PCK0oFyo Quiz 7 based on Chapter 13 will be at the end of the class. This will be our last quiz. |
Suggested exercises (for practice, not for grade): 1) Read Chapter summary 2) True/False questions: all 3) Mutliple Choice questions: 3-10 4) Short-answer questions: 1-5, 8, 9 5) Programming exercises: 1, 3, 5, 6, 9 No solutions nor answers are provided. |
|
| 05/09 | Sections 14.1 - 14.3 Terminology review (from CSI 35): CSI33-lecture24.pdf Lecture slides: CSI33-lecture24.pdf Dikstra's example: DijkstrasExample.pdf Breadth First Search implementation in C++: start by looking at an interface: BFS-interface.h, then grab the full solution: BFS.h, BFS.cpp, usingBFS.cpp, input1.txt Breadth First Search Demonstration (you tube, ~9 mins): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EuwG9nk0VxQ Dijkstra algorithm Demonstration (you tude, ~9 mins): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8Ls1RqHCOPw In-class Work: CSI33_Lecture24InClassWork.pdf |
||
| 05/04 | Section 13.3 Lecture slides: CSI33-lecture23.pdf programs (in C++): TreeNode.h, TreeNode.cpp, AVLTree.h, AVLTree.cpp, TestAVLTree.cpp programs (from the book, in Python): TreeNode.py, AVLTree.py, helpForAVL.py in-class work (with solutions): CSI33-AVL-In-Class-Practice.pdf, avl_handout-CSVirginiaEDU.pdf You can see all your grades in this Google Spreadsheet. Look into the row with the last four digits of your CUNY First ID (EMPLID). Quiz 6 is based on Chapter 7 will be at the end of the class Quiz 7 based on Chapter 13 material will be on Thursday, May 11th. This will be our last quiz. |
Suggested exercises (for practice, not for grade): 1) Multiple-Choice questions: p. 481 / 10 2) Short-Answer Questions: p. 481 / 2 3) AVL trees (Short Answer questions): page 481 / 4-11, Answers: Chapter13-AVL-answers.pdf 4) Look through the AVL code in Python and lecture slides - understand how the rotations are done. Finish up the AVL.py code. Comments: you can use the following code for testing/seeing what is happenning(just add it to your program) helpForAVL.py 5) Look through the AVL code in C++ thoroughly |
|
| 05/02 | Sections 13.3-13.5 in C++ Lecture slides: CSI33-Lecture22.pdf In-class work: CSI33-Lecture22_hashing.pdf programs (in C++): mapUse.cpp, UnorderedMapUse.cpp programs (from the book and not, in Python): HashLetter.py, test_HashLetter.py C++ map reference: http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/map/map/ |
Suggested exercises (for practice, not for grade): 0) Look through the hash examples in Section 13.5 1) True/False questions: p. 478 / 1, 2 2) Short-Answer Questions: pp. 479 - 480/ 1, 2, 4, 5, 8, 9 3) In-class work Answers: Chapter13-answers.pdf Self-study: starts on page 471 HashTable.py, test_HashTable.py (demonstrates hash table using chaining), HashTable2.py, test_HashTable2.py (demonstrates hash table using open addressing with linear probing) |
|
| 04/27 | Sections 13.1-13.2 Priority queues and heaps Lecture slides: CSI33-Lecture21.pdf programs: Heap.py, usingHeap.py, Heap.h, testingHeap.cpp In-class Work: see lecture slides, files to use: PQueue_ideas.py Answers/solutions: PQueue.py C++ map reference: http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/map/map/ Quiz 6 is based on Chapter 7 will be on Thursday, May 4th, at the end of the class |
HW10 (due date: Thursday, 05/11) - last HW assignment 1) programming exercises: p. 248 / 2, 3, 5 - you can do in C++ or in Python versions, it is your choice Python test code you can use for these problems: TestCodeForHWAssignment.py, for C++ use a similar one, Note that you are to add these "enhancements/additions" to our existing BST class definitions. Do not send me the code for these exercises separately from the BST we already did. 2) define the reverse operation for BSTs in Python implementations that will reverse the structure of the BST, i.e. for every node, all nodes in the left subtree have values greater than the value of the node; and all nodes in the right subtree have values less than the value of the node. Suggested exercises (for practice, not for grade): 1) Short Answer questions: p. 248 / 2, 3, 4 Solutions: Chapter7-questionsAnswers.pdf 2) Write unit tests for class BST to test insert_rec and find method, by doing the following: Insert the following elements, one by one into a tree: 7, 3, 8, 2, 5, 9, then by using BST's method asList compare the produced by that method list with list [2,3,5,7,8,9] - this is one unit test for insert_rec method. To test the find method: create the same BST as above, and find 8, 2, 9, and 5; compare the result with the numbers themselves. Then try to find 11, 1, and 4 and compare the result of each search with None. 3) Think of implementation of BST in C++. You can also start working on it. The suggested implementation will be posted later on. 4) define the delete operation for BSTs in the C++ code given above (use Python's code) |
|
| 04/25 | online meeting! The Zoom link in posted on the Blackboard Section 7.5 Lecture slides: CSI33-Lecture19.pdf programs (from the book): TreeNode.py, BST.py other programs: usingBST.py Useful links: BST delete node: http://www.algolist.net/Data_structures/Binary_search_tree/Removal Insertion and deletion (6 mins video): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wcIRPqTR3Kc Comment: deletion procedure here follows a different strategy: right subtree, leftmost element. In-class work: see lecture slides Solutions: CSI33Leture19InClassWorkSols.pdf, InClassWorkDay13.py Meeting recordings: part 1, part 2 , part 3 Quiz 5 is based on Chapter 6 will be at the end of the class - moved to Thursday, April 27th |
HW 9 (due date: Thursday, 05/04): Recall singly linked lists (in both, Python and C++),
i.e. every ListNode instance has two attributes: item and link.
Define a method reverse() of LList class (in either Python or C++ implementations of our LList class),
that would reverse the list. Here is an example (click on the picture to see it at a higher resoution): 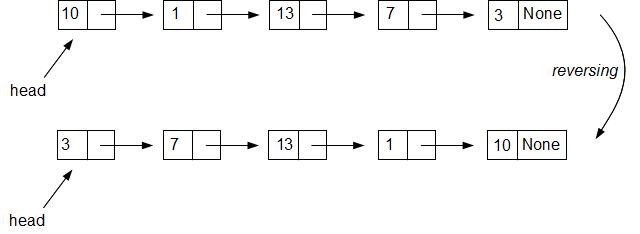 Suggested exercises (not for grade): 1) Short Answer questions: p. 248 / 2, 3, 4 Solutions: Chapter7-questionsAnswers.pdf 2) Write unit tests for class BST to test insert_rec and find method, by doing the following: Insert the following elements, one by one into a tree: 7, 3, 8, 2, 5, 9, then by using BST's method asList compare the produced by that method list with list [2,3,5,7,8,9] - this is one unit test for insert_rec method. To test the find method: create the same BST as above, and find 8, 2, 9, and 5; compare the result with the numbers themselves. Then try to find 11, 1, and 4 and compare the result of each search with None. |
|
| 04/20 | Sections 7.1-7.4 Lecture slides: CSI33-Lecture18.pdf programs (from the book): TreeNode.py The code we did in class: 1) we modified a bit the ListNode class in Python and added some testing: TreeNode2.py 2) then we worked on C++ code for ListNode: TreeNode.h, testing.cpp In-class work: CSI33_Day18_InClassWork.pdf ( we didn't do the last problem) Answers: CSI33Lecture18pics.pdf Quiz 5 based on Chapter 6 will be on Tuesday, April 25th, at the end of the class |
Suggested exercises (not for grade): 1) True-False questions: p. 245 / 1-5 2) Multiple-Choice questions: p. 246 / 2, 3 3) Short-Answer questions: p. 248 / 6 Solutions: Chapter7-questionsAnswers.pdf |
|
| 04/18 | Sections 6.4-6.6 Lecture slides: CSI33-Lecture17.pdf programs (from the book): mergeSort.py, hanoi.py Useful links: check out the online Tower of Hanoi puzzle You can watch a video on Merge Sort here: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Merge_sort Announcement: Our Final Exam is scheduled for Tuesday, May 23rd, from 2 pm to 3:50pm, at CP 320 |
HW8 (due date: Thursday, 04/20): - extended to Thursday, April 27th (1) Programming excercise: implement a template version of the average function (you may assume that we are planning to use it on the arrays of integers, floats and doubles only): average.cpp. (2) Programming excercise: p. 442 / 3 You must use these starters: TemplateList_forHelp.h, test_TemplateList.cpp the header file has all the declarations you'll need, so you only need to add missing definitions; the testing has a good enough testing code for you; another suggestion would be to put all the definitions that are missing into the header file (after the class declaration and the cin and cout declarations), then you don't have to create a file with extension .template - it seems to be a good way. Suggested exercises (for practice, not for grade): 1) True-False questions: p. 440 / 1, 2, 5 2) Multiple-Choice questions: p. 440-441 / 1, 2, 4 Answers: Chapter12questionsAnswers.pdf 3) Programming exercise: p. 442 / 2 Solution: Queue.h, testingQueue.cpp 4) Use our Python code (mergeSort.py) and write the definition of Merge Sort in C++, define it is a template function. Test it. 5) You can compare the running times of the Selection sort (selection.cpp) and Merge sort (use the definition you wrote and tested). You can put the code of both procedures in one header file, say sort.h, and then use them: test_sort.cpp, test_sort2.cpp. |
|
| Summarize all the data structures we explored so far with the run-time efficiency of common operations!!! You can see all your grades in this Google Spreadsheet. Look into the row with the last four digits of your CUNY First ID (EMPLID). |
|||
| 04/05 - 04/13 | Spring Break Our Final Exam is scheduled for Tuesday, May 23rd, same time and same place. |
||
| 04/04 | Sections 6.1-6.3 Lecture slides: CSI33-Lecture16.pdf programs (from the book): fact.py, reverse.py, anagrams.py, power.py, bsearch.py, fib.py In-class work: see lecture slides Solutions/answers: maxRec.py Quiz 4 today, based on Chapter 5 |
Suggested exercises: (for practice, not for grade): 1) What list is returned by anagrams("word")? 2) True-False questions: p. 212 / 1, 2, 3, 6 3) Multiple-Choice questions: p. 213 / 1, 4, 5, 6 4) Trace recPower(4,8) and and figure out exactly how many multiplications it does. 5) Short Answer questions: p.214 / 1, 5 6) programming exercises: p. 215 / 1, 5 Solutions: Chapter6Answers_part1.pdf, Chapter6Answers_part2.pdf |
|
| 03/30 | Sections 12.1-13.2 Lecture slides: CSI33-Lecture15.pdf programs (from the book and not): maximum.cpp, vec1.cpp, vec2.cpp, vec3.cpp Stack we defined before: Stack.h, Stack.cpp, StackTesting.cpp Template class Stack: Stack.h, StackTesting.cpp Reference manual for Vector class template: http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/vector/vector/ Algorithms library reference manual: http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/algorithm/ In-class Work: 1) Implement a template minimum function and test it on int and double type values. Solution: minimumInClassWork.cpp 2) Implement a Queue using templates along with the code to test it. This is a suggested HW assignment. Solution: Queue.h, testingQueue.cpp Quiz 4 based on Chapter 5 will be on Tuesday, April 4th, at the end of the class. |
HW 7 (due date: Thursday, 04/06) programming exercises: 1) p. 184 / 3 (use our implementation of Stack to evaluate the post-fix expression as shown in lecture slides), and 2) p. 184 / 4 (make sure to pay attention to all requirements in this exercise, you must use our implementation of the Queue) Suggested exercises: 1) True-False questions: p. 181 / 1-4 2) Multiple-Choice questions: p. 182 / 1-5 3) Short-Answer questions: p. 183 / 1 Answers/Solutions: Chapter5-questionsAnswers-part1.pdf, Chapter5-questionsAnswers-part2.pdf -------------------------------------- HW8 (due date: Thursday, 04/20): (1) Programming excercise: implement a template version of the average function (you may assume that we are planning to use it on the arrays of integers, floats and doubles only): average.cpp. (2) Programming excercise: p. 442 / 3 Feel free to use these starters: TemplateList_forHelp.h, test_TemplateList.cpp Comments: 1) the header file has all the declarations you'll need, so you only need to add missing definitions; 2) the testing has a good enough testing code for you to start with, but it doesn't test all the functions, so add more testing; 3) a suggestion: put all the definitions that are missing into the header file (after the class declaration and the cin and cout declarations), then you don't have to create a file with extension .template - it seems to be a good way. Suggested exercises (for practice, not for grade): 1) True-False questions: p. 440 / 1, 2, 5 2) Multiple-Choice questions: p. 440-441 / 1, 2, 4 3) Programming exercise: p. 442 / 2 Solution: Queue.h, testingQueue.cpp Answers: Chapter12questionsAnswers.pdf |
|
| 03/28 | Sections 5.3-5.5 Lecture slides: CSI33-lecture14.pdf programs (from the book): MyQueue.py, palindrome.py , C++ versions will be done in the next class meeting In-class work: see the lecture slides, CabCompany.pdf, TestingCab.py Solution: CabCompany.py Self-study: time-driven simulation: simulation.py, CheckerSim.py Event-driven simulation: simulationEventDriven.py, CheckerSimEventDriven.py Quiz 3 at the end of the class, based on linked lists (in both, Python and C++). |
||
| Summarize all the data structures we explored so far with the run-time efficiency of common operations!!! You can see all your grades in this Google Spreadsheet. Look into the row with the last four digits of your CUNY First ID (EMPLID). |
|||
| 03/23 | Sections 5.1-5.2 This will be online meeting, via Zoom. The Zoom link is posted on the Blackboard and was suppleied in the Blackboard announcement. Lecture slides: CSI33-lecture13.pdf programs (from the book): Stack.py, Stack.h, Stack.cpp, StackTesting.cpp, parensBalance2.py In-class assignment: see lectures slides. Solutions/answers: In-classWorkAnswers.pdf, Stackunittesting.py Quiz 3 at the end of the class on Tuesday, March 28th, based on linked lists (in both, Python and C++). After class meeting notes: 1) Here is the recording of Introduction to Stack 2) Here is the recording of going over Python code of Stack class 3) Here is the recording of going over C++ code of Stack class 4) Stack application: balanced parentheses check 5) Stack application: Infix - Prefix - Postfix notations 6) Stack application: Function call stack |
Check out these useful videos: Infix to Postifx: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rA0x7b4YiMI Infix to Prefix: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fUxnb5eTRS0 Suggested exercises: 1) Implement the balanced parentheses check in C++ |
|
| 03/21 | Topic: linked lists in Python and C++ Sections 11.1-11.5 (C++) Plan: today we will work on C++ implementation of linked lists Lecture slides: CSI33-lecture12.pdf Programs to use: ListNode.py, LList.py, testingLList.py, We did in class: LinkedList.h, LinkedList.cpp, Testing.cpp After class notes: 1) Look through the rest of the lecture slides 2) Methods need to be defined and tested: - copy constructor LList(const LList& source); - bracket operator (for both access and modification) ItemType& operator[](size_t position); - pop operator along with the helper method _delete ItemType pop(int i = -1); ItemType _delete(size_t position); Think about an implementation. If you want to practice, try to implement them. If you don't want to practice make sure to look over the complete code I will post on Friday. A solution: ListNode2.h, LList2.h, LList2.cpp, testList2.cpp 3) Prepare a table of time complexities of operations of LList class we defined. 4) Important: We might have an online meeting via Zoom on Thursday. The Zoom link is posted at the Blackboard. By Wednesday, 5pm I will send a message via Blackboard announcement with the final say: online or in-person. Quiz 3 on Tuesday, March 28th, based on linked lists (in both, Python and C++). |
HW 6 (due date: Thursday, 03/30) Programming exercise: p. 424 / 2 You can use this code to check that your program works correctly: Chapter11-testLList2.cpp. Feel free to add additional tests. Note that you are to work on our C++ source files. Modify, add methods, etc, but not start from scratch. Grab the files: ListNode2.h, LList2.h, LList2.cpp - work on them Suggested exercises (for practice, not for grade): 1) True-False questions: p. 422 / 1, 2, 5 2) Multiple-Choice questions: p. 423 / 1, 2, 4 3) Short-Answer questions: p. 424 / 1, 2 Solutions: Chapter11questionsAnswers.pdf |
|
| 03/16 | Midterm Exam The exam is closed book and closed notes, no smartphone use. Limited computer use will be allowed: you can only use in-class computers, and only the following applications: Python IDLE and Visual Studio. More details can be found on Midtem and Final Exams page |
||
| 03/14 | Review meeting Here are the sample questions: Spring2023-SampleQuestions Answers and solutions: Spring2023-SampleQuestions-Answers The code to the Part III will be posted on Wednesday morning. |
||
| 03/09 | Topic: linked lists in Python and C++ (continues) Sections 4.4, 4.5, 4.7 (Python) Lecture slides: CSI33-lecture11.pdf Programs: ListNode.py, LList.py, testingLList.py In-class work: see the last slide in the lecture slides |
HW 5 (due date: Thursday, 03/23) programming exercises: p. 152 / 1, 3 (do both in one file, LList.py) you can use this test code to test your program: Chapter4-prog1_3LList-testing.py You are to use the existing implementation of the linked list that we worked on. Suggested exercises: 1) True-False questions: p. 148 / 1, 2, 4, 5 2) Multiple-Choice questions: p. 149 / 1-4 3) take a look at two versions of __copy__ method for LList class's implementation on page 132. Solutions/answers: Chapter4-questionsAnswersSuggestedProblems.pdf 4) Short-Answer questions: p. 151 / 2 Answers: Chapter4-questionsAnswers.pdf 5) Complete all the in-class work |
|
| 03/07 | Topic: linked lists in Python and C++ Sections 4.1-4.3 (Python) Quiz 2 based on Chapters 2 and 3 and will be at the end of the class. Lecture slides: CSI33-lecture10.pdf Programs: Section4_2example.py, ListNode.py, LList (not finished) In- class work: see lecture slides 14 and 15, file to grab: Sections4_1-4_3InClassWork.py, Section4_2example.py Very useful read about classes, namespaces and many more: https://docs.python.org/3/tutorial/classes.html |
||
| 03/02 | Sections 10.4, 10.5 (we might need a separate class on memory management in Python and C++) Lecture slides: CSI33-lecture08-part2.pdf (we will continue implementaiton of List class in C++) programs that we finished in class: List.h, List.cpp, testingList.cpp Additional resources: 1)CPython List operations time complexity: https://wiki.python.org/moin/TimeComplexity 2) Python list documentation |
HW 4 (due date: Thursday, 03/09) Let's work on Rational class in C++. We will not need dynamical memory allocation, as rational numbers can be represented at fractions, a/b, where a in integer value and b is a non-zero integer value. Some part of the class definition is already in place. Grab these files and look through them thorougly: Rational.h, Rational.cpp, testingRational.cpp. You will see that the constructor, the copy constructor, the operation + and comparison operation < are defined, along with helper-methods. Note that operation + is defined as member method/function, and the comparison operation < is defined as standalone method. You are to continue working on this class to: 1) add three other basic operators - (subtraction), *(multiplication), and /(division) as member methods/functions of the class Rational (see the declaration and definition of addition operator +), see page 339 for their signatures; 2) add the five comparison operators <=, >, >=, ==, and != as standalone functions (see the declaration and definition of the > operator), see page 337 for their signatures; no need to define the input (>>) and output (<<) operators (they are written as standalone functions/methods), they are already defined for your convinience! Suggested exercises (not for grade, but highly recommended): 1) True-False questions: p. 100 / 2, 3, 6 2) Short-answer questions: p.102 / 1, 2, 3 Solutions: Chapter3-questionsAnswers-part1.pdf, Chapter3-questionsAnswers-part2.pdf Suggested project: page 104, programming exercise 9 |
|
| 02/28 | Sections 3.1, 3.2, 3.5, and 3.6 We will put aside the Deck and Card classes defined in Python, and move on to look at Python lists and implement a similar data type in C++! Lecture slides: CSI33-lecture08.pdf, CSI33-lecture08-part2.pdf (I don't think we will cover both sets of lecture slides, most likely we will continue the discussion in the next class) You can see your grades in this Google spreadsheet Quiz 2 will be based on Chapters 2 and 3 and will be on Tuesday, March 7th, at the end of the class. For self-development: Investigate two data types in Python: array and set in Python. |
||
| 02/20 - 02/24 | Monday, February 20th - BCC is closed. President's Day Tuesday, February 21st - runs on Monday schedule Thursday, February 23rd - no meeting for our class only, however you can meet to work on the following project together: Design and implement the card game given in this description in Python. This project is for extra points towards your HW scores. You can work on it in group, just in the comments put who was responsible for what. |
||
| 02/16 | Sections 3.3, 2.6 Lecture slides more programs (from the book): unitTestingCard.py Self-development: Section 3.4 talks about a Bridge game. You can read it and watch this nice video on how to play Bridge: rules: https://www.acbl.org/learn/ video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Tyd7KlsRYO4 another video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9yzS_26fICk Here is the code of the Hand.py |
HW 3 (due date: Thursday, 02/23) 1) Programming Exercises: p 103 / 1, 2, 3- all of these exercises should be implemented in one file Deck.py Test all the operations, send the tests with your HW submission! 2) Write unit tests to test the methods suit, suitName and rankNameof Card class in Card.py. Use Chapter2-unitTestingCardHW.py |
|
| 02/14 | Sections 2.1-2.3, and 3.3 from the book. Quiz 1 at the end of the class, based on Chapter 1, Section 1.3 material Lecture slides: CSI33-lecture06.pdf Programs: cardADT.py, test_cardADT.py, Card-spec.py, Card.py, testCard.py, Deck.py, testDeck.py |
||
| Homeworks, Midterm Exam and Final Exam warning: The homework, midterm exam, and final exam work must be solely your work. They are not for group work, they are not to be looked for the solutions in online resources. If I notice that your homework is similar to somebody else in our class, both parties' homework score will be zero (same for Midterm and Final Exam). If I notice that you found a solution in online resources, your score will be zero as well. Both cases, copying from somebody or finding and solution in online resources, are academic dishonesty. You will be given first and last warning. If I notice anything hapenning again, you will be reported to the chairperson and you may end up with a failing grade for this class. Academic Integrity Academic dishonesty (such as plagiarism and cheating) is prohibited at Bronx Community College and is punishable by penalties, including failing grades, dismissal and expulsion. For additional information and the full policy on Academic Integrity, please consult the BCC College Catalog. |
|||
| 02/09 | Chapter 1: Sections 1.1, 1.2. Lecture slides In-class work (with some answers): InClassPractice |
HW 2 (due date: Thursday, 02/16): Programming Exercise #9 , page 38 from Textbook (write it in Python) comments: 1) Write the program in Python, do not use any built-in stuctures other than Python list 2) Note that function squeeze should modify the original list by removing the duplicates 3) pay attention to everything you are asked to do! Suggested exercises (for practice, not for grade): 1) Look at your implementation of the Selection Sort (it was given as a suggested practice). What assymptotic running time does it have? Here is the running time analysis of the Selection Sort. 2) estimate the run-time complexity of the following block of code: # n is a positive integer s = 0 for i in range(n): for j in range(10): s += 1 3) estimate the run-time complexity of the following block of code: # the program finds a square root of n, if the answer is an integer value: n = int(input("Enter a positive integer:")) assert n >= 1 i = 1 while i * i <= n: if i * i == n: return i else: i+= 1 return "not an integer" 4) Look at the example of a simple statistics program (interface) on page 15 in the textbook 5) True/False questions: p. 33 / 4-6, 9, 10 - not for grade 6) Multiple Choice questions: pp.34-35 / 1-6, 10 - not for grade Solutions: Chapter1solsTFMConly.pdf 7) Short-answer questions: p. 36 / 8 - not for grade Solution: Chapter1ShortAnswerQuestions.pdf 8) read about docstring conventions at http://www.python.org/dev/peps/pep-0257/ 9) Watch a video about O, Ω, and Θ notations: https://youtu.be/6Ol2JbwoJp0 |
|
| 02/07 | Section 1.3 Lecture slides In-class work: InClassPractice Solutions: CSI33-Lecture05InClassPractice2-answers.pdf Additional materials: BinarySearchIllustrated.pdf Additional resources: Check out this simple explanation of big-O notation: https://medium.freecodecamp.org/big-o-notation-simply-explained-with-illustrations-and-video-87d5a71c0174 |
||
| 02/02 | Today we will talk about classes in Python and C++.
We will work on the class Complex of a complex number in its rectangular form (a+bi) Lecture slides Chapter involved: Chapter 9, section 9.1 programs we did in class: complex.h, testing.cpp; Complex.py, testing.py |
HW 1 (due date: Friday, 02/10): design and implement two classes: Book, Patron
(you can also implement Library class, but it is for practice, not for grade), following the guidelines presented here:
LibraryProject.pdf Important: * when submitting yor C++ code, it must compile in Microsoft Visual Studio (Code) * when submiting your Python code, it must be interpretable by Python Idle * if you are provided with the test code, make sure you use it and your program returns correct values * I will not debug your code, I will not be looking for the place where it is inccorrect. I will be running some test code to check that it returns correct values and works correctly. |
|
| 01/31 | Today we will work on a a program that reports some statistics about the data Lecture slides Handout Chapters involved: Chapter 1, Section 1.2.3 and Chapter 8, Section 8.12 the programs we did in class: stats.h, stats.cpp, testing.cpp; stats.py, testing.py (Python code is only started, not completed) |
For practice (not for grade): 1) implement the Selection sort (page 37, exercise 3) in both Python and C++. In your implementation: * define a function SelectionSort that takes two formal parameters: the array and its size (for C++ implementation use built-in C style array, assume that the capacity of the array is 100 elements), * In C++ version you may also assume that we are working only with integer values, but you can work with decimal numbers as well, just be consistent! 2) for the C++ implementation of the SelectionSort - re-write it as a template function. Feel free to use this handout: Selection Sort |
|
| 01/26 | Today is our first meeting. We will discuss: * assignment statements, * some built-in C++ types, * loops and control structures * lists in Python and arrays and vector class in C++ Lecture slides: we didn't do the binary search, this is a suggested practice Chapters involved: Chapter 8,Sections 8.3 - 8.12 programs we did: ProductAndAverage.cpp, productAndAverageOfThreeDecimals.py, productAndAverageOfThreeDecimals_withFunction.py, SumOfSquares.cpp (as a function), sumOfSquares.py, sumOfSquares_withFunctions.py, linearSearch.cpp (with built-in C-style array and with a vector), linearSearch.py | For practice (not for grade): Implement the binary search in both, Python and C++. In C++ implementation you have options for what sequental collection to provide as argument to the function call: a C-style array, a C++ array, or a C++ vector. |
|
| 01/23 | Hello and welcome to CSI 33 class. I plan to spend Jan. 26th, 31st and Feb. 2nd on Python and C++ languages review. It will be a brief review to make sure you understand what knowledge of C++ and Python is expected for our class. Make sure that you have both compilers available and ready to be used. We are going to use Python Idle and Visual Studio Community Edition C++ (select community edition from the drop down menu - please note that this is for Windows operating systems only) in class. The chapters 1, 2, 8, and 9 of the book are available through e-reserves: http://bcc-cuny.libguides.com/er.php?b=c Choose CSI33 from the list. This to give you time to get the textbook. |
Things to-do: 1) order the textbook 2) get the Python interpreter and C++ compiler, make sure they are working 3) I sent an email some time ago, stating the topics you learned in CSI 31, 32 and 35, that you will be using in CSI 33. Here is the pdf file. Read it, and make sure to address them. |
|